MOIRA Indoor Air Study
The MOIRA instrument is composed of 4 mini gas chromatography columns for compound separation and 2 mini mass spectrometers for compound identification and quantification. The instrument requires low-power, operates at 5-10 minute time resolution and is field-portable. The MOIRA system was recently deployed to a residential home in St. Louis, MO. The study focused on VOC chemical characterization and source apportionment of dozens of indoor pollutant sources and human activities. MOIRA identified and quantified hundreds of VOC molecules. An example time series of selected VOC’s during one of the study days is shown below. Individual-source chemical characterization is shown at the bottom of the page.
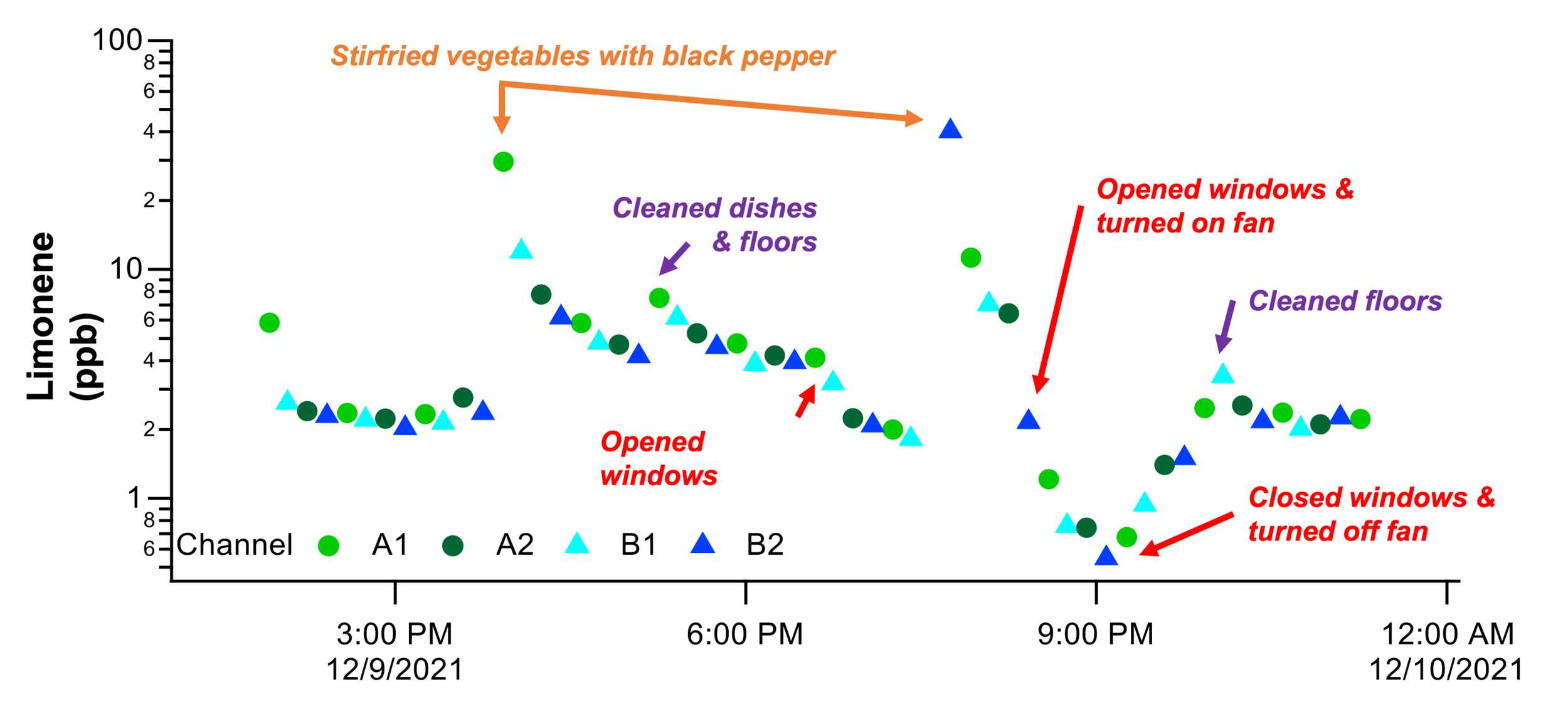
Above: example voc time series
10 minute time resolution GC/MS data was acquired by the MOIRA instrument during and indoor air study in St. Louis, MO. Hundreds of individual compounds were observed over dozens of introduced chemical and cleaning products, food cooking activities, window-opening practices, etc. Above is an example time series of one select VOC.
above: source-driven voc emissions
By viewing the trend of select major VOCs it can be seen that different sources and processes are driving differences and similarities across different chemical species. Covariance and grouping of compounds can be performed using statistical analysis methods. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) is currently being used to group covarying VOCs into source types or house activities.
above: Example chemical profiles of specific sources
Compounds associated with specific emission sources are seen during peak signal from various sources. Compounds associated with background house signal have been subtracted from the four examples shown above in order to provide a clear source profile.